2015 respirators ppe
-
Upload
john-newquist -
Category
Government & Nonprofit
-
view
502 -
download
0
Transcript of 2015 respirators ppe

Respirators
John Newquist
Draft 2 22 2015

Standard Overview
• Definitions
• Program
Requirements
• Selection
• Medical Evaluation
• Fit Testing
• Maintenance/Use
• Training
• Recordkeeping

Definitions PretestA. High efficiency particulate air
(HEPA) filter
B. Immediately dangerous to life
of health (IDLH)
C. Negative pressure respirator
D. Oxygen deficient atmosphere
E. Positive pressure respirator
F. Powered air-purifying
respirator
G. Self-contained breathing
apparatus (SCBA)
H. Supplied-air respirator (SAR)
I. Escape-only respirator
J. Tight-fitting facepiece

December 2014
• Evanston IL
• $132,000 to six contractors
• OSHA's inspection found that
onsite asbestos consultant
directed the HVAC contractor
to cut and remove 60 feet of
piping that contained asbestos
insulation without PPE. Typical asbestos pipe.

• PPE Assessment
• Payment
• Training
• Audit
Overview

Payment
• Employers pay for almost all personal protective equipment that is required by OSHA’s general industry standards.
• Metatarsal foot protection;
• Rubber boots with steel toes;
• Non-prescription eye protection;
• Hard hats/Bump Caps;
• Hearing Protection;
• Personal fall protection; and
• Reflective work vests.
• It does not require payment for uniforms, items worn to keep clean, or other items that are not PPE.
• Sturdy work shoes;
• Non-specialty slip-resistant, non-safety-toe footwear;
• Prescription Eye wear

Some Caveats
• PPE is used as a last resort
• The use of PPE signifies
that the hazard could not
be controlled by other
methods, such as:
– administrative controls (i.e.,
shift rotation)
– engineering or industrial
hygiene controls

Back to the caveats...
• The use of PPE signals that the
hazard still exists in the
workplace
• Unprotected individuals in the
same area will be exposed
• Failure of PPE means that the
worker will be exposed
• PPE can be combined with
other controls

Clean Air Paradox
• Quality of Air
• 78.1% Nitrogen
• 20.9% Oxygen
• 0.9% Argon
• 0.03% Carbon
Dioxide

Units Seem Small
1 % = 10,000 ppm
PEL = Permissible
Exposure Limits
(OSHA)
5 Mg/M3 is very small
2 f/cc = 2,000,000f/M3

Health Effects
• Irritation
• Asphyxiation
• Organ Specific Effects
• Mutagen
• Teratogen
• Acute/Chronic
• Reversible vs.
Nonreversible

Factors
• Genetics
• Age
• Health status
• Route of entry
• Frequency and
duration of exposure

Exposure Limits
• Animal Studies
• Epidemiological
studies
• Industrial Experience
• STEL – 15 minutes
• Ceiling – never
exceeded
• Threshold Limit Value

Sampling
• Qualified person
• Appropriate
instrument
• Duration of sampling
• Pre and post
calibration

Hierarchy of Controls
• Engineering
• Administrative
• Personal Protective
Equipment
• Training

Lead
• Requires compliance with 1910.1025
• Overexposure can occur in less than 5 minutes
when torch cutting or painting

Lead effects
• Chronic overexposure - severe damage to
the blood-forming, nervous, urinary, and
reproductive systems
• High levels will require medical removal
• Bridge Painting/Removal continues to be
ones of the consistent lead issues in
construction

Silica
• Cutting, hammering,
drilling, blasting can
create high silica
levels
• Use wet methods and
wear respirators
• One of the oldest
occupational diseases

Silica
• 150-200 deaths a year
(2009)
• 1150-1200 deaths a
year (1968)
• Yet….one company
had 3 silicosis and
10x+ severe
respiratory diseases
Gauley Bridge in 1920’s had
workers die in months.

Copper Fumes - Welding
• Copper is inhalation
hazard affecting
respiratory system
• Mild steel (red iron)
and carbon steel
contain manganese
• Manganese may
cause Parkinson's
disease What do you see?

Total Dust
• All the things not
regulated.
• Good, bad, or
indifferent?
• Air blowing!

Iron Oxide -Welding
• Metal fume fever
• Direct Draw or forced ventilation should be used
• Personal Protective Equipment should be used
• Bystanders should be protected as well

Carbon Monoxide
• Generators are most
common problem of
CO
• Heaters out of tune are
another cause
• CO TWA is 50 ppm
• Others set levels 25
ppm

Hex Chrome
• Stainless steel contains
nickel and chromium
• Plating, grinding,
welding are problems
• Some cements

Cadmium
• Overexposure to cutting cadmium bolts, coated poles
• Torch cutting should never be used
• Use hydraulic bolt cutters
• Comply with 1926.1127 Cadmium bolts are often
found in sprinkler pipe use.

Methylene Chloride
• Paint stripping
• Parts cleaners
• Cancer causing

Asbestos
• Common Fireproofing
material used pre-
1980s
• Found in pipe
insulation, ceiling
tiles, and floor tiles
• Must comply with
1926.1101 or
1910.1001

June 2014
• The asbestos lawsuit that
saw a $1 million award
• Richard Rost has
Mesothelioma
• Defendants included Ford
Motor Company (Ford),
General Electric,
Westinghouse and Ingersoll-
Rand.
• However, the latter three
defendants settled with the
plaintiffs out of court, before
the trial had an opportunity
to begin.
Overall, nearly 3,000 people
are diagnosed with mesothelioma each
year in the United States, which represents
0.02 percent of all U.S. cancer cases.

Respiratory
Protection
• 1910.134
– Written program #2
– Medical evaluation #1
– Fit testing #3, #6
– Selection, Evaluation of
exposure #5
– Maintenance, Storage, and
Care #9
– Annual Training #8
– Program evaluation #10
– Beards #7
Voluntary use App D - #4

Written Program Requirements
Program Elements:• Selection procedures
• Medical Evaluations
• Fit testing procedures for
tight-fitting respirators
• Proper use procedures -
routine & emergency
• Procedures & schedules for
maintenance
• Supplied air quality &
quantity
• Hazards Training - routine
& emergency
• Respirator use training
• Program auditing

Selection of Respirators
• Employer must select
and provide an
appropriate respirator
based on the respiratory
hazards

Uses/Limitations
• Will only work with corresponding filters or cartridges
• Can protect you from hazardous levels of materials
• If worn properly and in the right atmosphere, respirators can save your life

Uses / Limitations
Never use an air purifying respirator:
• If Oxygen level is below 19.5% or above 21%
• in an IDLH atmosphere;
• for ABRASIVE BLASTING;
• for FIRE FIGHTING;
• which is not APPROVED for the contaminant of concern;
• with FACIAL HAIR.

October 2014

Ebola

Ebola

On The Horizon
• Silica?
• Noise?
• Confined Space
in Construction?

Protection Factors

Respiratory protective equipment
Selection of suitable type
by competent personFactors:
• nature of hazards
• measured concentrations
• period of exposure
• vision
• communications
• confined spaces
• personal suitability

Respiratory protective equipment
Training in the use
of equipment must
be given
Stored in a clean
place with protective
enclosure

Respiratory protective equipment
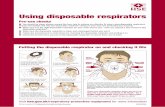
Disposable face mask:
• light, comfortable, cheap
• one user only
• eight hour maximum use, but
less if high dust levels
• dispose of after use
• May not be ok for silica
• Not for lead and asbestos

Respiratory protective equipment
Half-mask dust respirator:
• easily maintained
• freedom of movement
• may have ‘shelf life’
• colour coded cartridges

Anatomy of a half-mask respirator

Respiratory protective equipment
• High efficiency
particulate air (HEPA)
dust respirator:
• full face protection
• correct fitting and use
• beards, spectacles, etc.
may lessen efficiency

Respiratory protective equipment
Positive pressure powered
respirator:
• for long periods of work
• pump and filter
• approximately seven hours
use
• air leaks go outwards
• requires battery and filter
maintenance

Respiratory protective equipment
Helmet and visor respirator:
• battery-operated fan and
filter
• comfortable
• not for all hazards
• requires maintenance
schedules

Confined Space SAR

Self-contained Air Supply for
Escape.
Supplied air respirators are not
to be used in an atmosphere
which is immediately
dangerous to life and health
(IDLH) unless it is equipped
with a self-contained air supply
for escape.

Air Created by an Oil Lubricated
Compressor?
• For oil-lubricated compressors,
the employer shall use a high-
temperature or carbon
monoxide alarm, or both, to
monitor carbon monoxide
levels.
• If only high-temperature alarms
are used, the air supply shall be
monitored at intervals sufficient
to prevent carbon monoxide in
the breathing air from
exceeding 10ppm

Compressor Citation

Hose Length
• The total system
length can be up to
350 ft. with 100 ft.
maximum from the
pump to the
respirator and 250
ft. from the pump to
the inlet filter.

Respiratory protective equipment
Compressed airline breathing
apparatus:
• mask or hood with
compressed airline
• requires pure air at correct
pressure, humidity and
temperature
• air hose can restrict
movement

Respiratory protective equipment
Self-contained breathing
apparatus:
• mask, air regulator and
cylinder
• used only by a trained
person
• selected by competent
person
• cylinder duration is 20 – 30
minutes

Evaluation
• "The employer shall identify
and evaluate the respiratory
hazard(s) in the workplace; this
evaluation shall include a
reasonable estimate of
employee exposures to
respiratory hazard(s) and an
identification of the
contaminant's chemical state
and physical form
• Does not require air sampling
but……

Training Requirements
• Training must be provided prior to use
• Retraining is required annually, and when:– changes in the workplace
or type of respirator render previous training obsolete
– there are inadequacies in the employee’s knowledge or use
– any other situation arises in which retraining appears necessary

IDLH Training

Voluntary Use Requirements(other than filtering facepiece respirator)
• Medical evaluations
• Maintenance, Cleaning,
Storage
• Appendix D• The basic advisory information in
Appendix D must be provided to
employees who wear respirators
when use is not required by this
standard or by the employer

Voluntary Use Requirements
(Filtering facepiece only)
Appendix D only:
• Read and Heed all instructions
• Use approved respirators
• Properly selected
• Keep track of your respirator

#1 1910.134(e)(1)
• The employer shall provide a medical
evaluation to determine the employee's
ability to use a respirator, before the
employee is fit tested or required to use the
respirator in the workplace.
• The employer may discontinue an
employee's medical evaluations when the
employee is no longer required to use a
respirator

Medical Evaluation Requirements
• Evaluation completed prior to wearing respirator
• Annually thereafter
• Evaluation include information in Sections 1 and 2, Part 1
Of Appendix C
• Conducted by a physician or licensed health care
professional

Medical Signs and Symptoms
• The following are signs or
symptoms that may
prevent the use of a
respirator:
– Seizures
– Claustrophobia
– Asthma
– Emphysema
– Pneumonia
– Collapsed Lung
– Lung Cancer
– Broken Ribs
– Chest
Injuries/Surgeries
– Any other lung
problems
– Heart or Circulation
problems
– Anxiety

Fit Testing
Quantitative fit testing uses a machine to
measure the actual amount of leakage
into the face piece and does not rely
upon your sense of taste, smell, or
irritation in order to detect leakage
The fit test shall be administered
using an OSHA-accepted QLFT or
QNFT protocol.
Fit test not done before use. #6
Fit test not done annually #3

Fit Testing
• Qualitative fit testing is
normally used for half-
mask respirators - those
that just cover your mouth
and nose.
• Half-mask respirators can
be filtering facepiece
respirators - often called
"N95s" - as well as
elastomeric respirators.

TSI Qfit
• Qualitative respirator fit
tester is the only OSHA-
compliant (29CFR
1910.134) automated
pump-driven nebulizer for
Bitrex and Saccharin to
qualitatively test the
integrity of respirators to
the specific users wearing
them.

User Seal Check
An action conducted by the respirator
user to determine if the respirator is
properly seated to the face.
Positive Pressure
Check
Negative Pressure
Check

User Seal Check

Training
Requirements
• Training must be provided prior to use, unless acceptable training has been provided by another employer within the past 12 months
• Retraining is required annually, and when:– changes in the workplace or type of respirator render previous
training obsolete
– there are inadequacies in the employee’s knowledge or use
– any other situation arises in which retraining appears necessary
• The basic advisory information in Appendix D must be provided to employees who wear respirators when use is not required by this standard or by the employer

Employee Responsibilities
• Dirty respirator
• Wear PPE when necessary
and required
• Attend PPE training
sessions annually
• Care for, clean,
maintaining, and dispose
of PPE properly.
• Report any damaged or
defective PPE
immediately.

Respirator Defective

Cleaning Protocol
• Dismantle
• Wash
• Rinse
• Drain
• Sanitize
• Rinse
• Dry
• Reassemble
• Test
1. Hypochlorite solution or
2. Aqueous solution of iodine
or,
3. Other manufacturer
cleansers

Maintenance and Care
• Clean and disinfect at the following
intervals:
– as often as necessary when issued for
exclusive use
– before being worn by different individuals when
issued to more than one employee
– after each use for emergency respirators and
those used in fit testing and training

Storage
• Protect Respirator
from:
– Dust
– Sunlight
– Damaging chemicals
– Heat
– Extreme cold
– Excessive moisture

Inspection
• Dirt
• Cracks
• Tears
• Holes
• Distortion
• Broken parts
• Missing parts
• Elasticity
• Corrosion
• Valve test

Problems?

Questions?

Background
• Classes: OSHA 10/30 Hour,
Incident Investigation,
Confined Space, Excavation
Safety, Cranes Signaling and
Rigging, Fall Protection,
Scaffold Safety, and many more
• Services: Mentoring new safety
professionals, Mock OSHA
Inspections, Site Safety Audits,
OSHA Litigation Consultation,
Expert Witness, Reducing
Worker Compensation Risk,
Improving Site safety
76
• 34 years working with top
companies to achieve ZERO
injuries
• Certified Safety Professional
• OSHA 1983-2012
• Founding Member of ANSI Z359
• 815-354-6853




![Performance of Stockpiled Air-Purifying Respirators ... · PPE orders [DHHS 2012; NIOSH 2018]. To prepare for these shortages, large quantities of PPE are strategically stockpiled](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/5edde279ad6a402d66691c85/performance-of-stockpiled-air-purifying-respirators-ppe-orders-dhhs-2012-niosh.jpg)