20140120 Introduction and Radar Overview Pt 2
-
Upload
syed-umair-amer -
Category
Documents
-
view
230 -
download
2
Transcript of 20140120 Introduction and Radar Overview Pt 2

Week 2 - Session 3 1
Radar SystemsOverview
Week 2 – 3rd Session
20-Jan-14

Week 2 - Session 3 2
This Lecture
• The radar concept• The physics of electromagnetic waves
20-Jan-14

Week 2 - Session 3 3
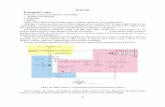
Radar Block Diagram
• Interaction with:• Atmosphere• Clutter• Targets
The Radar Concept
20-Jan-14

Week 2 - Session 3 4
Radar Block Diagram
The Radar Concept
Determining the presence of a target in the presence of noise,
clutter and jamming is a primary function of the radar’s signal
processor
20-Jan-14

Week 2 - Session 3 5
Most Important Attribute:– To measure distance with high accuracy and in all weather
The Radar Concept
20-Jan-14

Week 2 - Session 3 6
Target Range
The Radar Concept
20-Jan-14

Week 2 - Session 3 7
Interference:– Internal and external electronic noise– Reflected EM waves from objects not of interest (clutter)– Unintentional external EM waves created by other
human-made sources (EMI)– Intentional jamming from ECM system
• noise like receiver thermal noise• false targets like a true radar target)
The Radar Concept
20-Jan-14

Week 2 - Session 3 8
Means of Sensing
Attributes?
20-Jan-14

Week 2 - Session 3 9
Means of Sensing
20-Jan-14

Week 2 - Session 3 10
The Physics of EM Waves
EM waves are electric and magnetic field waves, oscillating at the carrier frequency.
20-Jan-14

Week 2 - Session 3 11
Wavelength, Frequency and Phase
The Physics of EM Waves
20-Jan-14

Week 2 - Session 3 12
Relationship Between Frequency and Wavelength
The Physics of EM Waves
20-Jan-14

Week 2 - Session 3 13
The Physics of EM WavesDifferent types of EM waves as function of frequency
• Radars operate in the range of:3 MHz – 300 GHz
• Large majority operate between about1 GHz – 35 GHz
20-Jan-14

Week 2 - Session 3 14
The Physics of EM Waves
20-Jan-14
Electronic Warfare (EW) BandsRadar Frequency Bands

Week 2 - Session 3 15
Phase and Amplitude
The Physics of EM Waves
20-Jan-14

Week 2 - Session 3 16
The Physics of EM Waves
Phase and Frequency
• Two sinusoidal waves with the same frequency but a phase difference ∆φ = 50 o
• If the waves are viewed as a function of time at a fixed point in space, then one isoffset from the other by ∆φ /ω
20-Jan-14

Week 2 - Session 3 17
Superposition (Interference)
The Physics of EM Waves
Concept of superposition in radar:• Formation of a defined beam produced by an antenna• Total radar cross-section (RCS) of a target due many scatterers• Effects of multipath
20-Jan-14

Week 2 - Session 3 18
Next Lecture
• Interaction of EM waves with matter• Basic radar configurations and waveforms• Basic radar configurations and waveforms• Noise, Signal-to-Noise ratio, and detection• Basic radar measurements• Basic radar functions• Radar applications
20-Jan-14