PRE-HISTORY PALEOLITHIC AND NEOLITHIC SOCIETIES TO THE RISE OF CITIES Adapted from: .
1.1 The First Peoples - · Objectives: What you should learn The spread of human societies in...
Transcript of 1.1 The First Peoples - · Objectives: What you should learn The spread of human societies in...

THE FIRST PEOPLESTO 10,000 BCE
APWH
Unit 1.1 - Technological and Environmental Transformations, c. 8000 B.C.E. to c. 600

Quick note on dates
BCE and CE
BC and AD
Eurocentric thinking
Muslim calendar marks year 1 in 622 CE with Muhammad’s emigration to Medina
China: dates by emperor reign

Objectives: What you should learn
■ The spread of human societies in the Paleolithic era
■ The conditions of life in gathering and hunting societies.
■ The factors that led to change in gathering and hunting societies.

Beginnings of Mankind
• Homo Sapiens appear around
250,000 years ago.
• Early humans formed groups of
hunter-gatherers (foragers) to get
food to survive.
• Everyone worked to survive.
• NomadicNomadicNomadicNomadic---- groups migrate (move
from place to place) when food
supplies run low.
Paleolithic – Old Stone Age. (250,000
BCE - 10,000 BCE)

Early Man (250,000-10,000 BCE)
■ Technological innovation – tools of stone and bone
■ Crafted tools to adapt to environments:
– Stone, bone, antler, wood materials.
– Axes, spears, arrows, fishing poles.
■ Adapted to environments - Clothing made from animals to survive.
■ Hunting-fishing instead of scavenging
■ Some groups were not able to survive on their own, exchanged peoples and ideas.
■ Most societies were egalitarianegalitarianegalitarianegalitarian- equal social roles between men and women.
■ Early period called the Paleolithic (Old Stone Paleolithic (Old Stone Paleolithic (Old Stone Paleolithic (Old Stone Age) Age) Age) Age)

■ Wrong to ignore 200K years of human experience.
– Archaeology reveals
■ Settled planet
■ Created earliest societies
■ First to reflect on the issues of life and death.

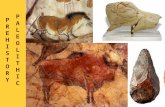
■ Earliest Europeans left cave paintings
– Myriad of speculative meanings:
■ “hunting magic”
■ Religion
■ ?
26K BCE
1700 BCE

Homo Sapiens
• 250K years ago Homo Sapiens
emerged in East and South
Africa
• Culture over biology begins to
shape human behavior.
• Humans begin moving to new
environments.

Human Migration Starting 100,000 Years Ago

■ Into the Americas 30K-15k years ago
– Land bridge?
■ Clovis people
– Hunted mammoths/bison
– Disappeared with large mammal extinction (10,900 years ago)
■ Replaced with more migrations over time.

■ New technologies upon reaching Ukraine/Russia
• To adapt to colder climate
– Needles, multilayered clothing, pottery.
– Homes made of mammoth remains
– Semi permanent settlement suggested.

■ Into Australia 60K BCE from Indonesia
– Boats
■ Sparse
■ Still hunting and gathering
– Complex worldview.
■ Dreamtime, ancestral beings, natural order an echo of the past, current people are related to the past
■ 3,500ya – into the Pacific.
– Took agriculture
– Organized societies
– Huge environmental impact.

THE WAYS WE WERE

First Human Societies
– Small, 25-50 people, kinship
– Low population density
– Paleolithic bands –seasonally mobile/nomadic
■ Patterned movement – food
■ No accumulation of goods

First Human Societies
– Highly Egalitarian
■ Perhaps most free in human existence.
■ No kings, bureaucrats, soldiers, priests
■ No specialists
– Male and female tasks differ
■ Male /female relationships more equal (women gather 70% of food)
■ Described as tranquil and socially equal by James Cook
– Clear rules
■ About distribution of meat, incest and ancestry

First Human Societies
■ Economy and environment
– Worked less, need little
– Low life expectancy (35)
– Set deliberate fires (to aid in hunting/foraging, protection, adaptation to cold)
– Extinction of large animals
– Extinction of other hominids12K ya, Honshu

First Human Societies
■ Spiritual realm
– Difficult to decipher.
■ Lack of written source
■ Art is subject to interpretation
■ Contemporary may not accurately reflect ancient exp.
■ Rich ceremonial life
– Part-time shamans
– Variety of beliefs
■ AnimismAnimismAnimismAnimism – plants, animals, other things have spiritual essence.

Settling down
■ Last Ice Age ends 16K-10K years ago– Warming period follows
– Neolithic Revolution (farming)
■ Settlement -> societal change -> large/complex societies ->storage and accumulation of goods -> inequality
– 12K-4K years ago– Major turn in human history.
THE NEOLITHIC REVOLUTION THE NEOLITHIC REVOLUTION THE NEOLITHIC REVOLUTION THE NEOLITHIC REVOLUTION ALONG WITH ITS AGRICULTURAL ALONG WITH ITS AGRICULTURAL ALONG WITH ITS AGRICULTURAL ALONG WITH ITS AGRICULTURAL REVOLUTION IS THE BIGGEST REVOLUTION IS THE BIGGEST REVOLUTION IS THE BIGGEST REVOLUTION IS THE BIGGEST THING THAT HAS SHAPED THE THING THAT HAS SHAPED THE THING THAT HAS SHAPED THE THING THAT HAS SHAPED THE WORLD IN TERMS OF WORLD WORLD IN TERMS OF WORLD WORLD IN TERMS OF WORLD WORLD IN TERMS OF WORLD HISTORY!HISTORY!HISTORY!HISTORY!
Catal Huyuk