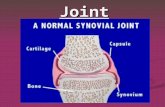
Things That Aren’t Muscles… Tendons, ligaments, and cartilage…
1 The Skeletal System. 2 Parts of the skeletal system – Bones – Joints – Ligaments –...
Transcript of 1 The Skeletal System. 2 Parts of the skeletal system – Bones – Joints – Ligaments –...

1
The Skeletal System

2
The Skeletal System• Parts of the skeletal system– Bones– Joints– Ligaments– Cartilage
• Divided into two divisions– Axial – longitudinal axis– Appendicular – limbs and girdles

3
Functions of Bones
• Support of the body• Protection of soft organs– Skull and vertebrae for brain and spinal cord– Rib cage for thoracic cavity organs
• Movement due to attached skeletal muscles• Storage of minerals (Ca+ and P) and fats• Blood cell formation (hematopoiesis)

4
Bones of the Human Body• The adult skeleton has 206 bones• Two basic types of bone tissue– Compact Bone – dense, looks smooth and
homogenous- Spongy Bone – needlelike
pieces of bone and open space
Figure 5.2b
Spongybone
Compactbone

5
Classification of Bones on the Basis of Shape
Figure 5.1
• Bones are classified as:– Long– Short– Flat– Irregular

6
Classification of Bones on the Basis of Shape

7
Classification of Bones• Long bones – longer than they are wide– Usually shaft w/head at ends– Limb bones except wrist and ankle– Mostly compound bone– Example: Humerus
• Short bones – cube shaped– Mostly spongy bone– Wrist and ankle– Sesamoid bones are a type of short bone which form
within tendons (patella)

8
Classification of Bones• Flat bones – Thin, flat and usually curved– 2 thin layers of flat compound bone sandwiching spongy
bone– Ex. Skull, ribs and sternum
• Irregular bones – miscellaneous– Vertebrae, hip bones

9
Gross Anatomy of a Long Bone
• Diaphysis – shaft of bone– Compact bone– Covered by connective
tissue called periosteum• Epiphysis – ends of
bone– Compact bone
surrounding spongy bone center
Figure 5.2a
Distalepiphysis
Diaphysis
Proximalepiphysis
Articularcartilage
Spongy boneEpiphyseallinePeriosteumCompact boneMedullarycavity (linedby endosteum)
(a

10
Structures of a Long Bone• Periosteum – connective
tissue covering diaphysis
• Sharpey’s fibers (perforating fibers)- hold periosteum to the bone
• Arteries – provide nutrients to bone cells and remove wastes
Figure 5.2c

11
Structures of a Long Bone• Articular cartilage –
covers the epiphyses– made of hyaline cartilage– Reduces friction at joints
• Medullary cavity – (yellow marrow)– Adults – a storage area
for adipose– Infants have red bone
marrow here** Red bone marrow in adults
is in spongy bone of flat bones and epiphyses of some long bones (pelvis, femur, etc.) Figure 5.2aFigure 5.2a
Distalepiphysis
Diaphysis
Proximalepiphysis
Articularcartilage
Spongy boneEpiphyseallinePeriosteumCompact boneMedullarycavity (linedby endosteum)

12
• Epiphyseal plate– Flat plate of
hyaline cartilage seen in young, growing bone
• Epiphyseal line– Remnant of the
epiphyseal plate– Seen in adult
bones
Anatomy of a Long Bone
Distalepiphysis
Diaphysis
Proximalepiphysis
Articularcartilage
Spongy boneEpiphyseallinePeriosteumCompact boneMedullarycavity (linedby endosteum)
(a)

13
Changes in the Human Skeleton
• In embryos, the skeleton is primarily hyaline cartilage– In a fetus the cartilage is covered over with bone and the
cartilage is digested, forming the medullary cavity
• During development, much of this cartilage is replaced by bone - ossification
• Cartilage remains in isolated areas– Bridge of the nose– Parts of ribs– Joints

14
Long Bone Formation and Growth
Figure 5.4a

15
Bone Growth (Ossification)• Epiphyseal plates allow for growth of long
bone during childhood– New cartilage is continuously formed– Older cartilage becomes ossified• Cartilage is broken down• Bone replaces cartilage
• Bones are remodeled and lengthened until growth stops– Bones change shape somewhat– Bones grow in width

16
Long Bone Formation and Growth
Figure 5.4bBone Remodeling Activity
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yFJ4iswRiu4&safe=active

Bone Markings• Surface features of bones– Sites of attachments for muscles, tendons, and
ligaments– Passages for nerves and blood vessels
• Categories of bone markings– Projections or processes—grow out from the
bone surface• Terms often begin with “T”
– Depressions or cavities—indentations• Terms often begin with “F”

18
Microscopic Anatomy of Bone
Figure 5.3

19
Microscopic Anatomy of Compact Bone
• Osteocyte – mature bone cells found in lacunae
• Osteon (Haversian System)– A unit of bone
• Central (Haversian) canal– Opening in the center of an osteon– Carries blood vessels and nerves
• Perforating (Volkman’s) canal– Canal perpendicular to the central canal– Carries blood vessels and nerves

20
Microscopic Anatomy of Bone
• Lacunae – cavity containing osteocytes (bone cells)
• Lamellae – circles of lacunae arranged around a central (Haversian) canal•Canaliculi – tiny canals
off of the central canal to the lacunae, provides each osteocyte with nutrient supplies

Figure 5.4c
Osteon
Lacuna
Centralcanal
Interstitiallamellae
(c)

22
Types of Bone Cells
• Osteocytes– Mature bone cells
• Osteoblasts– Bone-forming cells
• Osteoclasts—giant bone-destroying cells– Break down bone matrix for remodeling and release of
calcium in response to parathyroid hormone• Bone remodeling is a process by both osteoblasts
and osteoclasts• Bones are remodeled in response to Ca+ levels in the
blood and the pull of gravity and muscles
Rickets – disease where bones fail to calcify, legs bow out
-Caused by a lack of vitamin D
-Bones can also atrophy in bed ridden people