1 Chap 4 Defining The Project. 2 Chap 4 Step 1: Defining the Project Scope Step 2: Establishing...
-
Upload
mitchell-higgins -
Category
Documents
-
view
234 -
download
0
Transcript of 1 Chap 4 Defining The Project. 2 Chap 4 Step 1: Defining the Project Scope Step 2: Establishing...

1
Chap 4
Defining
The
Project

2
Chap 4
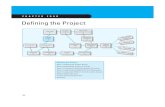
Step 1: Defining the Project Scope
Step 2: Establishing Project Priorities
Step 3: Creating the Work Breakdown Structure
Step 4: Integrating the WBS with the Organization
Step 5: Coding the WBS for the Information System
Steps in Defining Project

3
Chap 4
Defining the Project Scope
What you expect to deliver, when project is completed.
Project Objective: What, when and how much
Deliverables: Specific outcomes for each stage or milestone or review
Milestones: Major segments of the project
Technical requirements: Specific metrics which a deliverable must satisfy
Limits and Exclusions: What the project will not do
Reviews with Customers: Define frequency, provide direction, coincide with milestones & deliverables

4
Chap 4
Project Definition Example
Basketball game
Fashion Show
Taxi Service

5
Chap 4
Project Definition in Reality
Not well Defined• the more complex typically the less defined?• customer is unsure of what is possible, so they leave it general.
Scope Creep• adding slight changes to the project• impact is perceived to be minor but can be significant• especially prevalent in IT projects
Change control procedure is necessary• documents source of the change• defines specific change• defines impact on budget and time

6
Chap 4
Establishing Project Priorities
Project objectives center around satisfying Time, Performance & Cost.
These project factors can be at conflict? How?
Project Priority Matrix can help a Project Manager in making tradeoffs.
Time Performance Cost
Constrain
Enhance
Accept
Constrain: This factor must be meet, no compromise
Enhance: Optimize but can vary
Accept: Not meeting target is OK, within limits

7
Chap 4
Communication Plan
How to communicate status, changes, and performance
1. Identify Stakeholders
2. Define information required by each stakeholder
3. What are the sources for each form of information
4. Method of getting the information to the stakeholders
5. Who is responsible for placing the information in the correct format
and delivering it to the stakeholders.
6. What is the frequency of the information.
Plan is created by Project Manager in the early stages after discussion with team and stakeholders, in conjunction with WBS and OBS.

What is a WBS?What is a WBS?
A Work Breakdown Structure can show you at a glance:
What the various deliverables of the project are
How the necessary work is distributed between the project deliverables
How the cost or budget is distributed between the project deliverables
How the larger deliverables of the project are subdivided into smaller ones
But it does not say anything about individual tasks or the order of execution.
8
Chap 4

9
Chap 4
Creating the Work Breakdown Structure
Hierarchical approach of dividing the work by types; allowing a framework to track cost and work performance
Types: Frame, Plumbing, Electrical, Landscaping, HVAC, Drywall, Flooring
WBS follows the project structure not the functional organization
Output Oriented
Deliverables
Sub-deliverables :
Sub-deliverables
Cost Account
Work Packages
Costs rolled up
Com
munication

10
Chap 4
Coding the WBS for the Information System
Typically, WBS is coded beginning with Completed project and then indented until all Work Packages have been identified
Other forms of coding can be used to reflect different project structures. - Locations, functional depts, product type, customer, year, etc

11
Chap 4
Banquet Example

12
Chap 4
Product Development WBS Example

13
Chap 4
Project Definition Example
Basketball game
Fashion Show
Taxi Service

14
• A Work Breakdown Structure is not an exhaustive list of work
• A WBS is neither a project plan, a schedule, nor a chronological listing. • It is considered poor practice to construct a project schedule (e.g. using
project management software) before designing a proper WBS.
• A WBS is not an organizational hierarchy. • Some practitioners make the mistake of creating a WBS that shadows the
functional organizational chart.
• WBS updates, other than progressive elaboration of details, require formal change control.
• This is another reason why a WBS should be outcome-oriented and not be prescriptive of methods.
• A WBS is not a logic model. Nor is it a strategy map.
A Work Breakdown Structure is not:
Chap 4

15
• WBS includes 100% of the work defined by the project scope and captures all deliverables – internal, external, interim – in terms of the work to be completed, including project management.
• One of the most important principles guiding the development, decomposition and evaluation of the WBS.
• Applies at all levels within the hierarchy:
• The sum of the work at the “child” level must equal 100% of the work represented by the “parent” and the WBS should not include any work that falls outside the actual scope of the project, that is, it cannot include more than 100% of the work…
• It is important to remember that the 100% rule also applies to the activity level. The work represented by the activities in each work package must add up to 100% of the work necessary to complete the work package.
Practice Standard for Work Breakdown Structures (Second Edition), published by the Project Management Institute, ISBN 1933890134, page 8
The 100% RuleChap 4

16
Chap 4
Integrating the WBS with the Organization
Organizational Breakdown structure: Describes how the firm has assigned the work responsibility. - results from assigning of work packages responsibilities, made in WBS
When a dedicated project management structure is not used the OBS can: • help define and group the Cost Accounts by function• promotes communication of reporting and project changes
Same as WBS with the addition of functional departments matrices to WPs

Organizational Breakdown Structure (OBS)Organizational Breakdown Structure (OBS)
17
Project Mgr
Structural
ConcreteFramingMasonry
Interior
DrywallMuddersFinishingflooring
Plumbing
Water/SewerGas
Electrical
HookupOutletsWiringFixturesInfo Tech
Accounting
Marketing
Purchasing
Trucking
Project Oriented Structure
Chap 4

Organizational Breakdown Structure (OBS)Organizational Breakdown Structure (OBS)
18
Project Mgr
Accounting
ConcreteFramingMasonry
Info Tech Marketing Trucking
HookupOutletsWiringFixtures
Interior
Structural
Plumbing
Electrical
Roofing
Engineering
DrywallMuddersFinishingflooringWater/Sewer
Gas
Functional Structure
Chap 4

19
Chap 4
Project Definition Example
Basketball game
Fashion Show
Taxi Service

x x x
x x x
x x
x x
20
Responsibility Activity Matrix (RAM)
RAM is used to integrate the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) and the Organizational Breakdown Structure (OBS).
RAM output is Work Packages.
WBS
OBS
Chap 4

Work PackageWork Package
21
A work package at the activity level is a task that:
• can be realistically and confidently estimated;
• makes no sense practically to break down any further;
• can be completed in accordance with one of the heuristics defined above;
• produces a deliverable which is measurable; and
• forms a unique package of work which can be outsourced
• The activities listed in the work package are the activities listed in the MS Project plan.
• allows user to estimate costs for each task
Chap 4

22
Chap 4
1. Define work• Detail events• Specific deliverable(s)
2. Identify time to complete
3. Identify a time phased budget to complete
4. Identify a single person responsible for unit of
work
5. Identify monitoring points for measuring progress• How to measure a successful deliverable
Creating a Work Package
Lowest unit of WBS; This is where all the tasks are accomplished

23
• The “80 hour rule“: no single activity or group of activities to produce a single deliverable should be more than 80 hours of effort.
• Single Reporting Period: no activity or series of activities should be longer than a single reporting period.
• The "if it makes sense" rule. Applying this rule of thumb, one can apply "common sense" when creating the duration of a single activity or group of activities necessary to produce a deliverable defined by the WBS.
Level of DetailChap 4

$580 $300 $210
$600 $900 $950
$750 $450
$1860 $100
24
Responsibility Activity Matrix (RAM)
RAM output is Work Packages.
WBS
OBS
Create Menu 2 hrs $200Shop 4 hrs $250Prep 1 hrs $150Cook 3 hrs $ 200Serve 2 hrs $250
WP 1.2.4WP 1.2.3
Rent Tables $250Rent glass ware $200Rent silverware $200Setup 4 hrs $160
Chap 4

25
Chap 4
Assignment
Read and answer questions regarding
Manchester United Soccer Club case study.

Questions
26

27
Chap 4
Aircraft Example

28
1 SupportThis WBS element includes all management activities that typically span the entire project and are estimated in terms of level of effort rather than by reference to the specific work products produced. These include Program Management, Implementation (Release) Management, Logistics Management, and Technical Management. 11 Program ManagementThis WBS element includes all management tasks at the level of the entire project including organizing, directing, coordinating, and controlling all of the resources required to accomplish project objectives, cost/schedule performance management, subcontractor management, and quality management. 12 Implementation (Release) ManagementThis WBS element includes all of the effort to plan, control, and execute the implementation of all releases. 13 Logistics ManagementThis WBS element includes all of the effort to establish and maintain a logistics support and provisioning program, including, for example, supplies, storage, spares, and repairs of material used by the project. Material includes commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) software, and other tangible supplies. 14 Technical ManagementThis WBS element includes all of the effort to direct and control the technical engineering effort to transform the operational needs into a specification of requirements and an optimum configuration, including risk and issue management and configuration management.
WBS Dictionary (First Level)Chap 4











![Lecture 8. Lecture 8: Outline Structures [Kochan, chap 9] –Defining and using Structures –Functions and Structures –Initializing Structures. Compound.](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/56649e185503460f94b04bea/lecture-8-lecture-8-outline-structures-kochan-chap-9-defining-and-using.jpg)