1. 2-month old Stephanie uses her whole hand to grab for ...vanbiljon.yolasite.com/resources/SHMS02A...
Transcript of 1. 2-month old Stephanie uses her whole hand to grab for ...vanbiljon.yolasite.com/resources/SHMS02A...

1. 2-month old Stephanie uses her whole hand to grab for objects because she does not yet have good control of her fingers, suggesting which pattern of development?
A. cephalocaudal B. proximodistal C. encephalic D. primary
2. The process of encasing nerves with fat cells, which insulates nerves and helps electrical signals travel faster down the nerve, is referred to as
A. neuronal growth B. myelination C. lipidation D. insulation
3. Kenzi’s mother strokes his cheek and Kenzi turns his head toward the side of his face that was stroked, exhibiting which reflex?
A. stepping B. babinski C. moro D. rooting
4.__________________ control is a foundation for developing gross motor skills.
A. postural B. cognitive C. sensory D. perceptual
5. Who would be the oldest?
A. Adam, who can push his chest off the floor with his arms B. Bernie, who walks using furniture as support C. Dominic, who sits without support D. Lizzi, who tries to pull herself up on the side of the crib
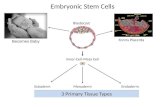
6. The period of prenatal development that occurs in the first 2 weeks after conception is called the ________________ period.
A. fetal

B. germinal C. embryonic D. blastocycstic
7. All of the following are periods of prenatal development EXCEPT
A. germinal B. embryonic C. fetal D. postpartum
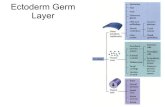
8. The embryo’s ______________ will develop into the digestive and respiratory systems.
A. mesoderm B. exoderm C. endoderm D. ectoderm
9. Language is most accurately defined as a system of_______________ that allows for communication with others.
A. signs B. symbols C. vocializations D. words
10. The most important mechanism newborns have for communicating with their world is
A. emotions B. facial expressions C. crying D. smiling
11. The _______________ principle of development suggest that growth begins at the center of the body and moves toward the extremes.
A. size constancy B. proximodistal C. cephalocaudal D. developmental biodynamics

12. An infant would use which of the following reflexes to obtain food?
A. rooting B. moro C. symmetrical tonic neck reflex D. eating
13. An infant will ______________ an object when it is placed in the palm of its hand.
A. grasp B. release C. extend D. throw E. non of the above
14. The approximate age of onset for a child to sit alone is during which month?
A. third B. fourth C. seventh D. eighth E. twelfth
15. When presented with a sudden, intense noise, the baby is startled and throws his arms up and to the side. This is an example of which reflex?
A. grasping B. rooting C. moro D. crying
16. Which is an example of a fine motor skill?
A. walking B. crawling C. radial palmar grasping D. bipedal locomotion
17. The 6 month old infant would most likely communicate with _______________.
A. babbling

B. simple sentences C. echo speech sounds D. name objects
18. For the average infant, social smiles appear as early as ________________ in response to adults.
A. 2 days B. 3 weeks C. 4 weeks D. 2 months
19. What is the second stage of Piaget’s cognitive theory of development that emphasizes a child’s ability to represent the world with words and images?
A. concrete operational B. zone of proximal development C. sensorimotor D. preoperational
20.Which factor is not associated with sensory awareness?
A. perception B. reception C. conceptualization D. undifferentiated crying E. expression
Match column A with Column B. (15)
Myelinization Involuntary response to a stimulus that is specific, purposeful and adaptive
Reflex Pulling with the arms and then pushing with legs while the abdomen is in contact with surface
Crawling Moving on hands and knees Creeping Transferring of info by some
symbolic form from 1 person to another
Communication Fatty substance that coats the nerve
Language Communication by means of voice Infant A child who can move

independently Toddler Fencing-like position Haptic sense A child who is not over 2 years Asymmetric tonic reflex Cell differentiation Germinal period Completely stops moving at 2weeks
before birth Embryonic period Unification Fetal period Gives meaning to the stimuli coming
to the brain by way of the sense organs
Considerable weight gain makes space confined
Embryo
Perceptual process Combination of feeling and movement
Most vulnerable period to viral diseases
Cell division
21. In a game of throwing a ball, a 6-year-old will
A. throw a ball by rotating the body and lower the throwing arm
B. throw a ball by stepping forward with the same foot as the throwing arm.
C. raise the arm above the level of the shoulder.
D. throw with the opposite foot stepping forward.
22. In a game of throwing a ball, a 2-year-old will
A. throw a ball by rotating the body and lower the throwing arm
B. throw a ball by stepping forward with the same foot as the throwing arm.
C. raise the arm above the level of the shoulder.
D. throw with the opposite foot stepping forward.
23. In a game of throwing a ball, a 3-year-old will
A. throw a ball by rotating the body and lower the throwing arm
B. throw a ball by stepping forward with the same foot as the throwing arm.
C. raise the arm above the level of the shoulder.
D. throw with the opposite foot stepping forward.
24. In a game of throwing a ball, a 6 ½ -year-old will

A. throw a ball by rotating the body and lower the throwing arm
B. throw a ball by stepping forward with the same foot as the throwing arm.
C. raise the arm above the level of the shoulder.
D. throw with the opposite foot stepping forward.
25. Raymond is learning to jump and kick. These skills demonstrate
A) gross motor skills.
B) fine motor skills.
C) minute skills.
D) operant skills.
26. By the age of 3 years, you would expect a child to
A. demonstrate alternate foot ascent of stairs.
B. kick effectively for distance and accuracy.
C. deal effectively with a rolling ball.
D. have a vocabulary of a 1000 words.
27. By the age of 5 years, you would expect a child to
A. demonstrate alternate foot ascent of stairs.
B. kick effectively for distance and accuracy.
C. deal effectively with a rolling ball.
D. have a vocabulary of a 1000 words.
28. By the age of 2 years, you would expect a child to
A. demonstrate alternate foot ascent of stairs.
B. kick effectively for distance and accuracy.
C. deal effectively with a rolling ball.
D. have a vocabulary of a 1000 words.

29. By the age of 4years, you would expect a child to
A. demonstrate alternate foot ascent of stairs.
B. kick effectively for distance and accuracy.
C. deal effectively with a rolling ball.
D. have a vocabulary of a 1000 words.
30. Darren is 7 years old, and loves to pretend that he is a fireman. He takes the garden hose and squirts water into the kitchen window. This is an example of what kind of play?
A) symbolic play
B) parallel play
C) associative play
D) solitary play
31. Kids playing a game of soccer are involved in what kind of play?
A) symbolic play
B) parallel play
C) associative play
D) solitary play
32. Gustavo and Hamza are on a play date. They are both sitting on the floor playing with blocks but they aren't really interacting with each other. This is an example of what kind of play?
A) symbolic play
B) parallel play
C) associative play
D) solitary play
33. Prince is playing with his new toys that he got for his birthday on the carpet. This is an example of what kind of play?
A) symbolic play

B) parallel play
C) associative play
D) solitary play
34. Carly is in the first grade and is developing skills for handwriting, coloring, and manipulating small objects like shoelaces and zippers. These activities are examples of
A) gross motor skills.
B) fine motor skills.
C) minute skills.
D) operant skills.
35. Zena has begun to scribble designs, telling her mother these are drawings of Daddy. She is also increasing her vocabulary and loves to play "pretend." She is in the:
A. preoperational stage
B. intuitive thought substage.
C. primary circular reaction substage.
D. sensorimotor stage.
36. Running is an example of a _________________ movement?
A. locomotor B. nonlocomotor C. fine motor skill D. projecting objects in space
37. The preoperational period is Piaget’s second stage of cognitive development and extends from about:
A. 2 to 4 years B. 2 to 7 years C. 4 to 9 years D. 3 to 10 years
38. The 7-year old child becomes ________________ because they realize that people are different

A. popular
B. self-critical
C. shy
D. proud
39. Increased myelination allow for greater
A. strength and accuracy
B. body awareness
C. body image
D. leadership
40. Strength in the young child can be best measured by
A. jumping
B. sprinting
C. grip strength
D. hold strength
41. A typical child that progresses through middle childhood, will experience all of the following EXCEPT
A. increased strength
B. increased agility
C. increased muscle tissue
D. increased reaction time
42. With the exception of skipping, jumping, and hopping, school-age boys
A. outperform girls in gross motor skills and in throwing and kicking B. continue to lag behind girls in other gross motor skills, such as throwing
and kicking C. have less confidence in their athletic abilities D. have better flexibility than girls

43. The period of middle and late childhood involves
A. slow, consistent growth B. rapid, consistent growth C. rapid spurts of growth D. moderate growth
44. Which statement in middle childhood is true
A. children need both dependence and autonomy B. family is more important than friends C. they tend to be more loyal towards their teachers than their friends D. criticism from both adults and peers are not taken to seriously
45. Locomotor skills during middle childhood display
A. mature patterns
B. immature patterns
C. basic learning
D. body awareness
46. Boys between the ages of 2 and 7 years have better __________________ than girls
A. balance and flexibility
B. strength and power
C. accuracy and endurance
D. speed and agility
47. Girls in middle childhood have better __________________ than boys
A. power
B. speed
C. gross motor skill
D. small muscle coordination
48. Preadolescence form their goals

A. passively B. through the influence of their peers C. by modelling themselves after other people D. by modifying earlier goals
49. The degree of maturation is commonly measured by
A. games and sports
B. Kaluger method
C. Meredith method
D. the extent of skeletal ossification
50. _____________________ is used to evaluate a child’s growth
A. games and sports
B. Kaluger method
C. Meredith method
D. the extent of skeletal ossification
51. A typical child that progresses through prepubescent period, will experience all of the following EXCEPT
A. increased body fat
B. increased strength
C. increased endurance
D. increased agility
52. David is 10 years old and doesn’t have many friends because his peers view him as
A. aggressive
B. different
C. average
D. popular

53. Earlier-maturing children achieve a somewhat higher level of peer acceptance and success because they are more
A. aggressive
B. friendly
C. cautious
D. physically skilled
54. Children who are different in some way or who play poorly may find they are ________________ by their peers
A. neglected
B. rejected
C. accepted
D. appreciated
55. The emotional characteristics of a 9-year old child include
A. one minute laughing, the next crying
B. easygoing and predictable
C. swings between sad and happy
D. sulking, crying a lot, outbursts of emotions
56. Boys during late childhood have better __________________ than girls
A. balance and flexibility
B. strength and endurance
C. accuracy and endurance
D. speed and agility
57. Girls in prepubescence period exceed boys of the same chronological age in
A. balance and flexibility
B. strength and endurance
C. accuracy and endurance

D. speed and agility
58. The major difference between girls and boys in late childhood is
A. physical ability
B. socialization
C. flexibility
D. culturalization
59. The emotional characteristics of a 10-year old child include
A. one minute laughing, the next crying
B. easygoing and predictable
C. swings between sad and happy
D. sulking, crying a lot, outbursts of emotions
60. The emotional characteristics of a 11-year old child include
A. one minute laughing, the next crying
B. easygoing and predictable
C. swings between sad and happy
D. sulking, crying a lot, outbursts of emotions
61. The belief that young boys should be strong, touch and daring is a __________________
A. social expectation
B. cognitive distortion
C. gender battle
D. freedom of action
62. Pat is described as friendly, sensitive and attractive. Pat’s gender role would best be described as _____________________
A. balanced

B. masculine
C. feminine
D. variable
63. Unsupervised play is far more ____________________ than that which is organized
A. enjoyable
B. dangerous
C. intense
D. beneficial
64. The Meredith method uses __________________ to plot normal channels of development
A. accuracy and endurance
B. ossification
C. age, height, weight
D. speed and agility
65. Feelings of physical inadequacy is usually experienced during
A. prepubescent period
B. middle childhood
C. adolescence
D. early childhood
66. The optimal time for participating in lifetime sports is
A. prepubescent period
B. middle childhood
C. adolescence
D. early childhood

67. Which statement about a friend is MOST likely to be made by a child in late childhood?
A. “She is my friend because she has better hair than me”
B. “We are friends because we walk to school together”
C. “Opposites attract”
D. “We share secrets”
68. Which statement about a friend is MOST likely to be made by a child in middle childhood?
A. “She is my friend because she has better hair than me”
B. “We are friends because we walk to school together”
C. “Opposites attract”
D. “We share secrets”
69. Laterality is well established in children during
A. prepubescent period
B. middle childhood
C. adolescence
D. early childhood
70. Criticism from both adults and peers peaks around which period?
A. prepubescent period
B. middle childhood
C. adolescence
D. early childhood
71. Between the ages of 9 and 10 years, children tend to play in
A. small groups
B. any group
C. loosely organized groups

D. specific groups
72. During middle childhood children tend to play in
A. small groups
B. any group
C. loosely organized groups
D. specific groups
73. Children in middle childhood play with ______________________ in their games
A. simple rules
B. complex rules
C. strategies and tactics
D. everyone
74. Children in late childhood play with ______________________ in their games
A. simple rules
B. complex rules
C. strategies and tactics
D. everyone
75. Children in early childhood play with ______________________ in their games
A. simple rules
B. complex rules
C. strategies and tactics
D. everyone
76. During early childhood, weigh gain follows the same pattern as
A. trunk

B. legs
C. height
D. head
77. Basic locomotor skills refer to
A. transporting one’s body in the upright position
B. fine motor skills
C. running, writing, hopping, painting
D. the extension of the walking pattern
78. Movement curriculum during early childhood places emphasis on
A. language
B. process and quality of movement
C. outcome of movement
D. skipping and galloping
79. Body awareness refers to
A. awareness of the environment
B. awareness of the body in stationary position
C. awareness of the body in space
D. awareness of the body’s two sides
80. Laterality refers to
A. awareness of the environment
B. awareness of the body in stationary position
C. awareness of the body in space
D. awareness of the body’s two sides
81. Playing peek-a-boo games will generally start at

A. 18 months
B. 5 months
C. 7 months
D. 3 months
82. During early development, sociality and __________ are closely associated
A. crying
B. smiling
C. emotions
D. play
83. ______________ indicates the infant’s response to discomfort
A. undifferentiated crying
B. frowning
C. vital crying
D. anger
84. The infant will follow a movement or object with the eyes when only
A. 4 weeks
B. 2 weeks
C. 3 months
D. 8 weeks
85. The head of the 2-year old child is approximately ______________ the size of the entire body
A. one-third
B. one-fifth
C. one-fourth
D. half

86. The head of the 5-year old child is approximately ______________ the size of the entire body
A. one-third
B. one-fifth
C. one-fourth
D. half
87. The most outstanding growth attribute of early childhood is the increase in
A. weight
B. locomotor skills
C. gross motor skills
D. height
88. Walking involves
A. one foot moves ahead of the other
B. the heal of the forward foot touches the ground before the toe of the opposite foot pushes off
C. arms & legs move in synchronous opposition
D. all of the above
89. The stages of running are
A. flight, push-off, landing
B. running, jogging, sprinting
C. step, hop, step
D. push-off, flight, landing
90. The prerequisites for climbing include
A. strength, balance, coordination
B. strength, agility, balance
C. endurance, balance, coordination

D. strength, reaction time, coordination
91. Alternate foot ascent of stairs is achieved at
A. 2 years
B. 3 years
C. 4-5 years
D. 5-6 years
92. Alternate foot descent of stairs is achieved at
A. 2 years
B. 3 years
C. 4-5 years
D. 5-6 years
93. The 2-year old child climbs up and down stairs with
A. lateral method
B. marking time pattern and unilateral method
C. coordination
D. lateral method and coordination
94. The neonatal period is
A. a period from birth to about 6 months
B. a period from birth to about 2 weeks
C. a period from birth to about age 2
D. a period from conception to birth
95. The fetal period is best described as a time when
A. major organ systems emerge from the less differentiated endoderm and mesoderm
B. support systems that sustain the fetus become fully formed and functioning

C. organ systems emerge
D. it is most vulnerable to impair development
96. Implantation marks the beginning of the
A. embryonic period
B. birth process
C. fetal period
D. germinal period
97. The heart and blood vessels develop from
A. endoderm
B. mesoderm
C. ectoderm
D. all of the above
98. Which is most likely to affect the child during the embryonic period?
A. maternal diabetes
B. herpes simplex
C. influenza
D. rubella