03 brachial plexus anatomy & blockade
-
Upload
red-bu -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
1.032 -
download
4
Transcript of 03 brachial plexus anatomy & blockade

Review of Brachial Plexus Anatomy &
Blockade

Review of Brachial Plexus Anatomy &
BlockadeRegional and APS Rotations

Review of Brachial Plexus Anatomy &
BlockadeRegional and APS Rotations

Review of Brachial Plexus Anatomy &
BlockadeRegional and APS Rotations
(Slides by Randall Malchow MD)

Brachial PlexusISB, SCB, ICB, and Axillary
n General Anatomy -’applied anatomy’n Anatomy and Techniques
n Interscalenen Supraclavicularn Infraclavicularn Axillary

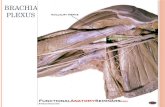
C5-T1 Nerve RootsAnt and Mdl ScalenesSubclavian ArteryMid-clavicleCoracoid Process“Sheath”
BrachialPlexus
n General Anatomy

Brachial Plexus in situAnt and Mdl ScalenesPhrenic NerveVertebral ArterySubclavian VeinMid-Clavicle and 1st Rib
NB: relation of B.P. to 1st part of Ax Art

C5
C6
C7
C8
T1
-“Hour Glass”-4 Approaches to BrPl

Rule of 3’sn Roots:
n Phrenic (C3,4,5)n Lg Thoracic (C5,6,7)n N.s to Strap m.s
n Upper Trunk:n Dorsal Scapn Suprascap (C5,6)n Lat Pectoral (C5,6,7)
n Post Cord:n Upper Subscapn Lower Subscapn Thoracodorsal
n Med Cord:n Med Pectoraln Med Brachialn Med Antebrachial

+
*nerve leaves atcoracoid process
**
**
Supraclavicular Branches
Serratus Anterior
Lat Dorsi
Pect Maj
Pect Min
Infraclavicular Branches
Supra/infraspinatus/75% shoulder joint
Rhom/LevScap
Subscap/TerMaj(Outside Sheath)

BrachialPlexusn Distal
Anatomy

Sensory:Dermatomes
(Nerve


Sensory:Peripheral
NerveDistribution
Lat Antebrachial Cutan N
n Note: Medial Brachial Nerve Not Shown

Biceps/BrachialisCoracobrachialis
FlexionSupination

4. Elbow Extension5. Supination (Brachio- radialis;supinator)

4. Pronation-Pron Teres/Quad


Interscalene Techniques:n History:
n Kappis, 1912, Posteriorn Mulley, 1919, Ant,
immobilen Classic N. Stim:
n Avoid These Muscle Stim Patterns:
§ Serratus Ant (Lg Th)§ Rhomboid/Lev Scap (Dors
Scap)§ Trapezius (XI)§ Diaphragm (Phren)
n USGn Posterior ISB:
n “Cervical PVB”n Excellent for ISB Caths

Interscalene Approach:Surrounding Structures
*
*
*

*Surface Anatomy and Technique:Pos’n (head, arm)At C6 level, IS groove, 2-3cm post to SCM(NB: EJ, and posterior location)

If too deep, anterior:

Interscalene Approach- othern Limitations:
n Minimal Blockade of Lower Trunk (C8,T1) (w/ >40ml may get lower trunk)
n Poor approach for surgery distal to shoulder
n If awake, know the operation
n Cath difficult (placement/dislodge)
n Indications:n Shoulder Surgery- esp
openn Proximal humeral or
scapular fx’s, othern Initial Block Eval:
n “Money sign”n “Deltoid sign”n “Triangle Sign”

Posterior Cervical Paravertebral Blockn Alternate approach for ISBn Advantages:
n Avoids anterior vascular structures: Vert artery, carotid, ext jugular, etc
n Less phrenic nerve block?; improved diaphragm function.
n Less catheter leaking, dislodging, etcn Catheter not in surgical prep area.

Ant Scalene Muscle
Mid Scalene Muscle
Brachial Plexus
Levator Scapulae Ms.
Trapezius Muscle
Vertebral Artery
Carotid Artery
Internal Jugular Vein
Posterior Cervical PVB

Levator Scapulae Muscle
Sternocleidomastoid MuscleTrapezius Muscle
Splenius Capitus

Sitting position; C6 Level

Direct needle anterior, medial, and caudal towards suprasternal notch, until C6 transverse process reached. Walk needle off laterally using LOR or needle stimulation to Brachial Plexus.

Interscalene Approach
Distribution:
Will miss med antebrachial

Interscalene ApproachComplications
n SAB/Epiduraln Intravascular - vert art
leading to sz’sn Other Nerve Blockade:
n Phrenic: 100%n Recurrent Laryngeal:
hoarseness 10-20%n Stellate Ganglion:
horner’s syndrome 25-50%
n Bezold Jarisch/vagal: esp right isb 10-20%
n Seizures 0.7%n Cough/bronchospasmn Pneumothorax - rare

Supraclavicular Approach
n History:n Kulenkampff, 1911n Adv inf, med, post; paresthesia
techn Indications:
n Excellent for elbow and forearm surgery
n Good for hand and wristn Special considerations:
n Pneumothorax: 0.1-5%n Franco: 1001 SCB’s: no
pneumothoraxn Phrenic Nerve
Blk: 40%

C5,6
C7
C8,T1
AnteriorPosterior
PSPectoralis Major
Pectoralis Minor
Subclavius

Supraclavicular – Classic vs USG*Position
of pt and doc.
1-2cm from SCM or widthof clavicular head away.
SCM

Supraclavicular Techniques- Desired Stimulationn Avoid:
n Shoulder stimulationn Upper trunk stim: (musculocutaneous)
n Aim for stimulation:n Franco: 97% success w/ distal twitchn Subclav Art “pushes” local towards upper trk
n If cough, too deep (against pleura)

variable
Supplement ICBN
Supra-clavicularSpread

Infraclavicular Approachn Overview:
n Intent: Blockade distal to pleura, prox to branches (ie block at level of cords)
n History: n Bazy 1917; Labat 1927
(aiming med.)n Raj, 1973 (aiming
lateral)
n Indications:n Excellent for forearm/
wrist/hand surgeryn Popular location for
brachial plexus catheter

Infraclavicular Approach:n Advantages:
n >success w/ MC, Med Brachial & Antebrachial nerves compared to traditional AXB;
n Intercostobrachial often blocked
n Min phrenic block/pneumothorax risk
n Arm in any position
n Disadvantages:n ? Benefit over USG
Axillary block with > riskn Difficult to see needle at
steep anglesn < Patient Satisfaction?
(deeper block)n Sml < success
compared to AXB? (94% vs 99%)

InfraclavicularApproachAnatomy:
n Landmarks:
n Jugular Notchn AC Jointn Deltopectoral
Grooven Pectoral Major
m.n Deltoid m. n Cephalic Vein

Biceps-short head
Coracobrachialis
Pect.minorSubscapularis
Teresmajor
Lateral Cord (C5,6,7): MC. & medianMedial Cord (C8,T1): Ulnar, median, med brach and antebrachPosterior Cord (C5-T1): Radial & Axillary
(90% lat to CP)
(65% lat to CP)
ICB:n Specific
Anatomy

Infraclavicular Approach:techniques
n Nerve Stimulationn Lateral Direction/Raj:
n Mid-clavicle aiming laterallyn Vertical /Coracoid process:
n Wilson 1998: aim directly posterior n Single vs Multi-nerve stim
n USG

RajTechnique
n Arm at 90 deg
n 21 gu x 4inn Mid-clavicle
entry, 45 deg to skin
n Aim laterally towards ax art
n Depth: ave 4.5cm
n CPNB

Pect MajorDeltoid
Subscapularis
Pect minor
Lung
RajTechnique:
n Safety of infraclav approach
n Axillary boundariesn Anteriorn Posteriorn Medial

CoracoidProcess
Technique:n 2cm med
& inf to coracoid
n 21 gu x 4in
n Aim post:n If lat to CP,
could miss MC/ Ax n.s.
n Depth: ave 4cm (2-7cm)

Infraclavicular Approach: Desired stimulation
n Goal: distal twitch in wrist or hand n Lateral Cord: avoidn Medial Cord: median/ulnar okn Posterior Cord: radial ideal
n Upshot: n flex or ext wrist/digitsn Extension bestn Consider multi-stim

Axillary Approach
n History: n Hirschel, 1911
n 4in needle to 1st ribn Pitkin, 1927:
n 8in needle to trans proc!
n 1950: > popularityn 1989: Ting, USG

Axillary Block - continuedn Indications:
n Hand and wrist surgeryn Elbow/forearm w/
multistim/ USG techn Goal:
n simple brachial plexus anesthesia at most distal point to avoid complications
n Advantages:n > 98% successn > Very high Pt satisn Exc USG imagingn Short MC block vs Long
duration AXBn Disadvantages:
n > needle movement? n Arm at 90 deg

AxillaryAnatomy
n Pyramid shapen (-)MC, Ax, Med
brach and antebrach
n Neurovasc bundle lying atop the lat dorsi/ teres m.
n Between coracobrach. and triceps

Axillary Approach:Cross sectional anatomy
n Note relationships of:n Bicepsn Coracobrachialisn Long Head of
tricepsn Musculocutaneous
nerve route thru coracobrachialis (variable)
n Lateral: M&Mn Medial: U&R
Long head of triceps
Medial head of triceps
Deltoid

Techniques of Axillary Approachn 1. Transarterial
n Either all posterior (Urmey)
n or 50% post, 50% antn 2. Single Nerve Stimn 3. Paresthesian NB: No difference in
1st 3 tech, all 80% (Goldberg)
n 4. Multiple Nerve Stimulation(2-3)n Quick onsetn < LA toxicity riskn < Hematoma riskn > Success >95%
n 5. Ultrasound – ideal technique
n NB. > 98 % success w/ these 2 techs

Mult Nerve Stim AXB(3 injections)
n 5mm above and below artery
n M/M on top
n U/R below
15ml
15ml
10ml

Axillary Approach
Supplementation
n If operating above elbow
n Not needed for tourniquet
n Medial Brachial Nerve, T1
n Intercostobrachial T2 (not part of brach plex)
n Subcutaneous infiltration above and below sheath

Axillary Distribution
n Good coverage of:n Ulnarn Mediann Radialn Musculocutaneousn Medial antebrachial
n Supplement prn:n ICBNn Med Brachial
Will capture MCN with separate injection