Produce skeletal movement By contraction of muscle fibers True of all = cardiac, smooth, skeletal ...
-
Upload
abigayle-lang -
Category
Documents
-
view
222 -
download
1
Transcript of Produce skeletal movement By contraction of muscle fibers True of all = cardiac, smooth, skeletal ...

Notes: Functional Anatomy of Muscles

1. What are the six functions of the muscular system?
Produce skeletal movement By contraction of muscle
fibers True of all = cardiac,
smooth, skeletal Maintain posture/body
position Some muscles are always
“on” – fight against gravity Support Tissues/Stabilize
joints Shoulder joint is VERY
unstable – needs muscle and tendons to keep it steady

1. What are the six functions of the muscular system?
Maintain Body Temp/Generate heat Large amount of energy is
given off as heat during muscle contraction
Guard Entrances and Exits Openings of tracts
encircled by skeletal muscles
Store Nutrient Reserves Muscle broken down when
there is an inadequate amount proteins

2. What are the 3 types of connective tissues found in muscles? What structure does each one surround? Epimysium
Surrounds entire skeletal muscles
separates muscles from tissues and organs
Perimysium Surround
muscle fascicle Endomysium
Surround muscle fibers

3. Components of a skeletal muscle fiber:
Sarcolemma The cell
membrane of a muscle fiber
Sarcoplasm Cytoplasm of a
muscle fiber Transverse Tubules
Narrow tubes continuous with sarcolemma
Passageways that the action potential travels through

3. Components of a skeletal muscle fiber:
Myofibrils Bundles of
myofilament Separated by
sarcoplasmic reticulum
Contractile orgalles of skeletal muscle
Extend entire length of muscle fiber

3. Components of a skeletal muscle fiber:
Myofilaments Bundles of
myofilament Separated by
sarcoplasmic reticulum
Contractile orgalles of skeletal muscle
Extend entire length of muscle fiber

Myofilaments Contractile proteins of the muscle Thick and thin filaments overlap
each other in a pattern that creates striations I band – only thin filaments
Figure 6.3b
3. Components of a skeletal muscle fiber:

3. Components of a skeletal muscle fiber:
Myofilaments continued
The protein fibers that actually compose the myofibrils
Thick filaments Made of protein
myosin Cross bridges link
to thin filaments Thin filaments
Made of protein actin

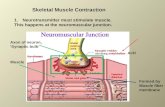
Sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) fluid-filled system of
membranous sacs surrounds each
myofibril stores Ca2+
Release of calcium into Sarcoplasm signals the beginning of a muscle contraction Figure 6.3a
4. What is the sarcoplasmic reticulum? What is its role in a muscle contraction?

Basic functional unit of a myofilament A band (darker) – extends the entire
length of thick filaments I band (lighter) – thin filaments thin
ments Proteins that stabilize the filaments Proteins that regulate the interaction
between filaments
5. What is a sarcomere? What are the four things it contains?

A band (dark band)
M-line: central part of the
thick filament stabilize position of
thick filament H-zone: Contains thick
filaments only Zone of overlap: Where the think and
thick filaments overlap
6. Components of a sarcomere:

I-band (light band)
Z-lines: Boundaries
between sarcomere
Titin: Elastic protein Keeps filaments in
proper alignment Helps muscle fiber
resist extreme stretching
6. Components of a sarcomere:

During a muscle contraction thin filaments are sliding toward the center of each sarcomere
Sliding occur within every sarcomere in a muscle fiber
7. What is the sliding filament theory?

When a skeletal muscle fiber contracts
The H zones and I bands get smaller
The zones of overlap get larger
The Z lines move closer together
The width of the A band remains constant
7. What is the sliding filament theory?