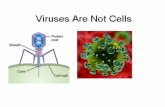
Non-living: Need a host to reproduce Lysogenic Cycle: break out of the cell when reproduction is...
-
Upload
imogene-nicholson -
Category
Documents
-
view
213 -
download
1
Transcript of Non-living: Need a host to reproduce Lysogenic Cycle: break out of the cell when reproduction is...

MicroorganismsBacteria, Fungi, Viruses, and Protists

Viruses
Non-living: Need a host to reproduce Lysogenic Cycle: break out of the cell
when reproduction is finished. Lytic Cycle: Can remain dormant for
long periods of time; then enters lysogenic cycle.
Causes HIV, Flu, Chicken Pox, HPV, Colds

Virus Examples

Bacteria
Two kingdoms:› Archaebacteria: extremophiles› Eubacteria: some cause disease; useful in
food production (yogurt, cheese) Shapes:
› Rod (Bacillus)› Circle (Coccus)› Spiral (Spirillum)

Bacteria Examples
Streptococcus
StaphylocuoccusSpirillum

Protists
Anything not considered bacteria, fungi, or virus.
Single or colonial. Can move by cilia, flagella, or
pseudopods. Some plantlike (photosynthesize);
Others animallike (heterotrophic)

Protist Examples

Fungi
Some unicellular Decomposers and Saprobes (feed off of
living things) Mushrooms, Yeast, Molds Used to make bread and alcohol Penicillin made by a mold.

Fungi Example