Histology: The study of Tissue Tissue: a group of cells and their intercellular substances...
-
Upload
bernard-clarke -
Category
Documents
-
view
232 -
download
0
Transcript of Histology: The study of Tissue Tissue: a group of cells and their intercellular substances...
Histology: The study of TissueHistology: The study of Tissue
Tissue: a group of cells and their Tissue: a group of cells and their intercellular substances (matrix), intercellular substances (matrix), specialized and together performing a specialized and together performing a specific functionspecific function
4 tissue types4 tissue types
1.1. Epithelial tissueEpithelial tissue: (epithelium) covres and : (epithelium) covres and lines body surfaces and cavities, or forms lines body surfaces and cavities, or forms secretory portion of glandssecretory portion of glands
2.2. Connective tissueConnective tissue: supports the body, binds : supports the body, binds body and organs together or transports. body and organs together or transports. (C.T.) (C.T.)
3.3. Muscular TissueMuscular Tissue: contracts, movement: contracts, movement4.4. Nervous TissueNervous Tissue: initiates and transmits nerve : initiates and transmits nerve
impulses controlling the body by coordinating impulses controlling the body by coordinating and integrating activitiesand integrating activities
Epithelium: General Epithelium: General CharacteristicsCharacteristics
1.1. Composed of closely packed cells with Composed of closely packed cells with little or no extracellular matrix, arranged little or no extracellular matrix, arranged in sheets, may be layeredin sheets, may be layered
2.2. Are avascular ( no blood vessels). The Are avascular ( no blood vessels). The get nutrients and dispose of waste by get nutrients and dispose of waste by diffusion from underlying connective diffusion from underlying connective tissue.tissue.
3.3. Are attached to a layer of connective Are attached to a layer of connective tissue by way of nonliving, adhesive tissue by way of nonliving, adhesive basement membranebasement membrane
Basal lamina:Basal lamina: glycoprotein (glue) secreted glycoprotein (glue) secreted by epithelial cellsby epithelial cells
Reticular laminaReticular lamina: contains reticular fibers : contains reticular fibers from connective tissuefrom connective tissue
4.4. Are highly regenerative ( still capable of Are highly regenerative ( still capable of mitosis)mitosis)
Can replace by cells lost by abrasion or Can replace by cells lost by abrasion or hostile substances (acids, smoke, hostile substances (acids, smoke, bacteria etc..)bacteria etc..)
Functions of Epithelial Functions of Epithelial tissuetissue
1.1. Covering and liningCovering and lining Covers external body surfaceCovers external body surface Lines cavitiesLines cavities Covers internal organsCovers internal organs
2.2. GlandularGlandular: forms secreting portion of : forms secreting portion of glands glands
Classification of Epithelial Classification of Epithelial tissuetissue
Based on 2 characteristics: shape and Based on 2 characteristics: shape and layerslayers
Shape:Shape: 1. 1. squamous:squamous: flattened, scale-like flattened, scale-like 2. 2. cuboidalcuboidal; cube shaped; cube shaped 3. 3. columnar:columnar: rectangular solid rectangular solid 4.4.transitionaltransitional: combination of above, : combination of above,
Since they are subject to stretchingSince they are subject to stretching
LayersLayers
1.1. simple:simple: one layer, generally specialized one layer, generally specialized for absorption or filtration and not for absorption or filtration and not subject to wear and tearsubject to wear and tear
2.2. StratifiedStratified: stacked or layered, generally : stacked or layered, generally protective in abrasive areaprotective in abrasive area
3.3. Pseudostratified:Pseudostratified: appears to be appears to be stratified but the cells from only one stratified but the cells from only one layer. Lines much of the respiratory layer. Lines much of the respiratory tract tract
Classification/functionsClassification/functions
1.1. Simple:Simple: major function is for major function is for absorption and secretionabsorption and secretion
2.2. Stratified:Stratified: major function is for major function is for protectionprotection
classificationclassification FunctionFunction LocationLocation
Simple squamousSimple squamous Diffusion, osmosis, Diffusion, osmosis, filtrationfiltration
Lungs, kidneys, Lungs, kidneys, heartheart
Simple cuboidalSimple cuboidal Secrete/absorbSecrete/absorb Kidney, thyroidKidney, thyroid
Simple columnarSimple columnar Secrete/absorbSecrete/absorb Lines digestive Lines digestive tract, uterustract, uterus
Stratified squamousStratified squamous protectprotect skinskin
Stratified cuboidalStratified cuboidal protectprotect Rare, sweat glandsRare, sweat glands
Stratified columnarStratified columnar protectprotect Rare, male urethraRare, male urethra
psuedostratifiedpsuedostratified secretesecrete Respiratory tractRespiratory tract
transistionaltransistional stretchstretch bladderbladder
Epithelial adaptationsEpithelial adaptations
Absorption cellsAbsorption cells: have microvillie ( folds : have microvillie ( folds to increase surface area. Ex simple col to increase surface area. Ex simple col epep
Goblet cellsGoblet cells: mucus secreting cells, may : mucus secreting cells, may have cilia to keep things movinghave cilia to keep things moving
GlandGland
One cell or group of highly specialized One cell or group of highly specialized epithelial cells that secretes substance into epithelial cells that secretes substance into ducts, onto a surface or into bloodducts, onto a surface or into blood
Classification:Classification: 1.1. Exocrine:Exocrine: secretes substance directly into secretes substance directly into
duct.duct.2.2. Endocrine:Endocrine: secretes substance directly into secretes substance directly into
bloodblood
Glands may also be Glands may also be described asdescribed as
1.1. UnicellularUnicellular: in humans only goblet cells: in humans only goblet cells
2.2. Multicellular:Multicellular: have have 3 shapes3 shapes
a.a. TubularTubular
b.b. Alveolar or flask likeAlveolar or flask like
c.c. Tuboalveolar ( both shapes combined)Tuboalveolar ( both shapes combined)
Glands may also be Glands may also be classified by how they classified by how they
discharge their productsdischarge their products1.1. MerocrineMerocrine: discharge secretory material from : discharge secretory material from
the cell by exocytosis without harming cell ex the cell by exocytosis without harming cell ex sweat glands, salivary glandssweat glands, salivary glands
2.2. Apocrine:Apocrine: part of cell pinches off enclosing part of cell pinches off enclosing secretory product, remainder of cell repairs secretory product, remainder of cell repairs itself. Ex mammary glanditself. Ex mammary gland
3.3. Holocrine:Holocrine: cell keeps accumulation product cell keeps accumulation product until ruptures and dies or is secreted. Ex oil until ruptures and dies or is secreted. Ex oil glandgland
Connective TissueConnective Tissue
Most abundant and varied tissueMost abundant and varied tissue Generally few, widely spaced cells with large Generally few, widely spaced cells with large
amount of matrixamount of matrix Highly vascular ( except cartilage)Highly vascular ( except cartilage) Does onto occur on free surfaceDoes onto occur on free surface The matrix determines the tissue qualities ( it is The matrix determines the tissue qualities ( it is
non living and varies from fluid blood plasma to non living and varies from fluid blood plasma to rubbery cartilage matrix to bonerubbery cartilage matrix to bone
4 Classes of C.T.4 Classes of C.T.
1.1. Connective tissue properConnective tissue proper
2.2. CartilageCartilage
3.3. Blood (vascular)Blood (vascular)
4.4. Bone (osseous)Bone (osseous)
Fibers ( 3 types found in Fibers ( 3 types found in matrix of C.T.)matrix of C.T.)
1.1. CollagenousCollagenous: (white) strongest fiber, : (white) strongest fiber, consists of parallel bundles of a protein called consists of parallel bundles of a protein called
collagencollagen Are flexible but do not stretch or branchAre flexible but do not stretch or branch2.2. Elastic fibersElastic fibers: ( yellow): ( yellow) ( smaller branching fibers made up of a protein ( smaller branching fibers made up of a protein
called called elastinelastin ) ) does stretch like rubberdoes stretch like rubber3.3. Reticular fibers:Reticular fibers: thin, highly branched fibers, thin, highly branched fibers, made primarily of collagen, forms a “net-like mesh”made primarily of collagen, forms a “net-like mesh”
Cell Types ( appearing in C.T.)Cell Types ( appearing in C.T.)
““blast”:blast”: immature cell, actively forming immature cell, actively forming somethingsomething
““cyte”:cyte”: mature, less active cell mature, less active cell So you can have: fiberblast (cytes)So you can have: fiberblast (cytes) chondroblasts (cytes)chondroblasts (cytes) asterblast (cytes)asterblast (cytes) hemocytoblast (cytes) hemocytoblast (cytes)
Connective tissue proper:Connective tissue proper:
Has 2 other cell typesHas 2 other cell types::
1.1. MacrophagesMacrophages: seek out and eat foreign : seek out and eat foreign matter and dead cellsmatter and dead cells
2.2. Mast cellsMast cells: fight infection by secreting : fight infection by secreting heparin ( anticoagulent) and histamine ( heparin ( anticoagulent) and histamine ( dilute blood vessel)dilute blood vessel)
Types of C.T.Types of C.T.
Connective Tissue Proper: TypesConnective Tissue Proper: Types1.1. Areolar C.T.: most widely distributed, Areolar C.T.: most widely distributed,
has all 3 fiber types. has all 3 fiber types. Found primarily between epithilium and Found primarily between epithilium and
the muscles or organs it covers, also the muscles or organs it covers, also between muscle groupsbetween muscle groups
Connective Tissue Proper: TypesConnective Tissue Proper: Types
2.2. Adipose C.TAdipose C.T. : really just areolar tissue . : really just areolar tissue with numberous with numberous adipocyteadipocytes (fat cells). s (fat cells). It is adapted for lipid storage. Usually It is adapted for lipid storage. Usually found with areolar C.T. under epidermis found with areolar C.T. under epidermis where it insulates, pads and serves as where it insulates, pads and serves as a vital food reserve a vital food reserve
Connective Tissue Proper: TypesConnective Tissue Proper: Types
3.3. Dense C.T.Dense C.T. : called dense because it is : called dense because it is mostly fibers closely packed with less fluid in mostly fibers closely packed with less fluid in the matrixthe matrix
2 types:2 types:a.a. Irregular: Irregular: fibers run in all directions forming fibers run in all directions forming
sheets (fascia) covers bone, musclessheets (fascia) covers bone, musclesb.b. Regular:Regular: fibers run in one direction can fibers run in one direction can
withstand tension in one direction. Found in withstand tension in one direction. Found in tendons, ligaments and aponeurosestendons, ligaments and aponeuroses
a.a. TendonsTendons: connect muscle to bone: connect muscle to bone
b.b. LigamentsLigaments: bone to bone: bone to bone
c.c. AponeurosesAponeuroses: connect muscle to : connect muscle to muscle or bonemuscle or bone
Connective Tissue Proper: TypesConnective Tissue Proper: Types
4.4. Elastic C.TElastic C.T.: dense arranged C.T. but .: dense arranged C.T. but fibers are free branching. Found in fibers are free branching. Found in vocal cords, around major arteries and vocal cords, around major arteries and joining vertebraejoining vertebrae
5.5. Reticular C.TReticular C.T.: Delicate network of .: Delicate network of reticular fibers forming an internal reticular fibers forming an internal framework of some organs framework of some organs (spleen,liver)(spleen,liver)
Aereolar Connective Aereolar Connective TissueTissue
Know: Know:
FiberblastFiberblast Collagenous Collagenous
fibers fibers Elastic fibersElastic fibers
Reticular Connective Reticular Connective TissueTissue
Know:Know: Reticular cellsReticular cells Reticular fibersReticular fibers
Types of C.T.Types of C.T.
2.2. CartilageCartilage: sort of ½ way between dense C.T. : sort of ½ way between dense C.T. and boneand bone
Contains Contains chondrocyteschondrocytes (produce collagenous (produce collagenous fibers and end up surrounding themselves with fibers and end up surrounding themselves with fibers and matrix and live in spaces called fibers and matrix and live in spaces called lacunae)lacunae)
Cartilage has no blood supply or nerve supply Cartilage has no blood supply or nerve supply and receives its nourishment by diffusion from and receives its nourishment by diffusion from perichondriumperichondrium. .
Thus slow to heal and does so imperfectly ( tends Thus slow to heal and does so imperfectly ( tends to mineralize: bony with age or damage) to mineralize: bony with age or damage)
Types of C.T.Types of C.T.
3.3. Blood:Blood: Connective tissue with fluid Connective tissue with fluid matrix (plasma) matrix (plasma)
Has fibers but doesn’t solidify until Has fibers but doesn’t solidify until clottingclotting
More next semesterMore next semester
3 Types of cartilage3 Types of cartilage
1.1. Hyaline:Hyaline: most abundant and weak most abundant and weak Found in the ends of long bones, ends Found in the ends of long bones, ends
of ribs, the nose, trachea and of ribs, the nose, trachea and embryonic skeletonembryonic skeleton
2.2. FibrocartilageFibrocartilage: strongest, very dense: strongest, very dense
Found in : knew joints, disc between Found in : knew joints, disc between vertebrae, disc between pelvic bonesvertebrae, disc between pelvic bones
3 Types of cartilage3 Types of cartilage
3.3. Elastic cartilageElastic cartilage: has elastin fibers: has elastin fibers Found in: ear and estachian tubes and Found in: ear and estachian tubes and
epiglottisepiglottis
Types of C.T.Types of C.T.
4.4. Osseous Tissue (bones):Osseous Tissue (bones): Connective tissue with widely seperated cells Connective tissue with widely seperated cells
called called osteocytesosteocytes Matrix composed of collagen fibers and Matrix composed of collagen fibers and
inorganic calcium saltsinorganic calcium salts Has a vascular system with blood vessels Has a vascular system with blood vessels
running through running through haversioan canalshaversioan canals and and canaliculia( serving lcanaliculia( serving lacunasacunas with with osteocytes)osteocytes)
Hyaline CartilageHyaline Cartilage Know:Know: LacunaeLacunae Rubbery matrixRubbery matrix chondrocyteschondrocytes
Elastic CartilageElastic Cartilage
KnowKnow
LacunaeLacunae Elastic fibery Elastic fibery
matrixmatrix chondrocyte chondrocyte
Osseous Tissue (bones):Osseous Tissue (bones):
Functions:Functions: Support and protect soft tissueSupport and protect soft tissue Point of muscle attachment’Point of muscle attachment’ Stores mineralsStores minerals Produces most blood cellsProduces most blood cells
Muscle TissueMuscle Tissue
Highly cellular and vascularHighly cellular and vascular FunctionsFunctions: : movement, movement, maintenance of posture,maintenance of posture, production of heatproduction of heat
HistologyHistologyThe Study of the microscopic The Study of the microscopic structures of tissuesstructures of tissues
Histological Grouping Histological Grouping of Tissueof Tissue
1. Epithelial Tissue1. Epithelial Tissue 2. Connective Tissue2. Connective Tissue 3. Muscle3. Muscle 4. Nervous Tissue4. Nervous Tissue
Epithelial TissueEpithelial Tissue
Tissue that covers a body surface Tissue that covers a body surface or lines a body cavity.or lines a body cavity.
Is named based on two criteria: Is named based on two criteria: 1. Cell shape 1. Cell shape 2. Cell layers2. Cell layers Functions in: Functions in: protection,protection, absorptionabsorption, , filtrationfiltration, , excretion/secretionexcretion/secretion and as and as
a a sensory receptorsensory receptor
Cell LayersCell Layers
1. 1. SimpleSimple: one cell layer: one cell layer
2. 2. StratifiedStratified: two or more cell layers: two or more cell layers
3. 3. Pseudostratified:Pseudostratified: one cell layer but one cell layer but looks as if it has several layer .looks as if it has several layer .
Cell ShapeCell Shape
1.1. Cuboidal :Cuboidal : cubed shaped cellscubed shaped cells
2. 2. Columnar:Columnar: column shaped cells column shaped cells
3. 3. Stratified Stratified: : flat scale shaped cellsflat scale shaped cells
Epithelial Slides CoveredEpithelial Slides Covered
On ALL SLIDES BE On ALL SLIDES BE ABLE TO IDENTIFY ABLE TO IDENTIFY THE TYPE OF TISSUE THE TYPE OF TISSUE AND KNOWAND KNOW::
• CELL MEMBRANE, CELL MEMBRANE, • CYTOPLASM CYTOPLASM • NUCLEUSNUCLEUS
Slides coveredSlides covered 1. Simple squamous 1. Simple squamous
epitheliumepithelium 2. Simple cuboidal 2. Simple cuboidal
epitheliumepithelium 3. Simple columnar 3. Simple columnar
epitheliumepithelium 4. Pseudostratified 4. Pseudostratified
ciliated columnar ciliated columnar epithelium epithelium Know:Know: cilia, cilia, goblet cellsgoblet cells
5. Stratified squamous 5. Stratified squamous epitheliumepithelium
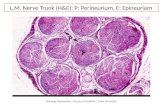
Connective TissueConnective Tissue
The most abundant and widely The most abundant and widely distributed tissuedistributed tissue
Functions in: binding and support, Functions in: binding and support, protection, insulation and protection, insulation and transportationtransportation
Characterized by having few cells Characterized by having few cells scattered about a nonliving matrix.scattered about a nonliving matrix.
Aereolar Connective Aereolar Connective TissueTissue
Know: Know:
FiberblastFiberblast Collagenous Collagenous
fibers fibers Elastic fibersElastic fibers
Hyaline CartilageHyaline Cartilage Know:Know: LacunaeLacunae Rubbery matrixRubbery matrix chondrocyteschondrocytes
Elastic CartilageElastic Cartilage
KnowKnow
LacunaeLacunae Elastic fibery Elastic fibery
matrixmatrix chondrocyte chondrocyte
Reticular Connective Reticular Connective TissueTissue
Know:Know: Reticular cellsReticular cells Reticular fibersReticular fibers
MusclesMusclesDivided into 3 categories:Divided into 3 categories:
1.1. Skeletal:Skeletal: voluntary, striated, voluntary, striated, multinucleated, peripherally located. Body multinucleated, peripherally located. Body movement and posture movement and posture
2.2. Smooth:Smooth: involuntary, not striated, 1 involuntary, not striated, 1 nucleus. Found in walls of hollow organsnucleus. Found in walls of hollow organs
3.3. Cardiac:Cardiac: striated, involuntary, 1 nucleus striated, involuntary, 1 nucleus heart heart
Nervous TissueNervous Tissue
The functional unit of nervous tissue The functional unit of nervous tissue is the neuronis the neuron
NeuronsNeurons
NeuronsNeurons: specialized to receive a stimulus : specialized to receive a stimulus and convert it to an impulse and conduct it onand convert it to an impulse and conduct it on
Are the functional units of the nervous systemAre the functional units of the nervous system Has 3 parts:Has 3 parts:
1.1. PerikaryonPerikaryon: cell body: cell body
2.2. Dendrite:Dendrite: short carries info to perikaryon short carries info to perikaryon
3.3. Axon:Axon: long, carrier info away from perikaryon long, carrier info away from perikaryon
Neuroglial cellsNeuroglial cells
Cells which support, protect, nourish and Cells which support, protect, nourish and insulate the neuron insulate the neuron
Membranes: Membranes: multicellular multicellular sheets of 2 tissue typessheets of 2 tissue types
1.1. Epithelial membraneEpithelial membrane: consist of a : consist of a sheet of epithelium and underlying layer sheet of epithelium and underlying layer of C.T.of C.T.
2.2. Synovial membraneSynovial membrane:: No epithelial tissueNo epithelial tissue Are layers of aereolar and adipose C.T.Are layers of aereolar and adipose C.T. Covers tendons and lubricate and Covers tendons and lubricate and
nourish with synovial fluidnourish with synovial fluid
Epithelial membraneEpithelial membrane
Composed of: Composed of:
1.1. MuscosaMuscosa: wet epithelial membrane : wet epithelial membrane which lines body cavities opening to which lines body cavities opening to exterior. Usually secrete mucus. Ex exterior. Usually secrete mucus. Ex digestive, respiratory, reproductive tractdigestive, respiratory, reproductive tract
2.2. Cutaneous membranesCutaneous membranes: (skim) Dry : (skim) Dry epithelial membrane ( integumentry)epithelial membrane ( integumentry)
Epithelial membraneEpithelial membrane
3.3. Serosa:Serosa: wet membranes which line close wet membranes which line close body cavitiesbody cavities
Consists of parietal layer (lines cavity wall) Consists of parietal layer (lines cavity wall) and visceral layer (covers organs)and visceral layer (covers organs)
So serosa have names according to locationSo serosa have names according to location:: PleuraPleura: lines thoracic wall and lungs: lines thoracic wall and lungs Pericardium:Pericardium: encloses heart encloses heart PeritoneumPeritoneum: lines abdominopelvic cavity and : lines abdominopelvic cavity and
organsorgans