{ Connective Tissue 1. Specialized Cells 2. Extracellular protein fibers 3. Ground substance=fluid.
-
Upload
percival-may -
Category
Documents
-
view
217 -
download
1
Transcript of { Connective Tissue 1. Specialized Cells 2. Extracellular protein fibers 3. Ground substance=fluid.

{{
Connective TissueConnective Tissue1.1. Specialized CellsSpecialized Cells
2.2. Extracellular protein fibersExtracellular protein fibers
3.3. Ground substance=fluid Ground substance=fluid

Connective Tissues Connective Tissues Characteristics Characteristics
•Most diverse tissues of the bodyo CT never exposed to the outside
environment •Abundant extracellular matrix•Varying degrees of vascularity•Contain sensory receptors

Connective Tissue Connective Tissue FunctionsFunctions
• Support & Protection
• Transportation of Materials
• Storage of Energy Reserves
• Defense of the Body

Connective Tissue Connective Tissue Major Cell TypesMajor Cell Types
Fibroblasts• Fixed cell• Most common cell • Large, star-shaped cell• Produce fibers & GS
Macrophages• Wandering cell• Specialized for phagocytosis• Important in defense
Mast cells• Small, mobile •Found near blood vessels • Release chemicals to begin chemical defense
Fat cells•Adipose cells•Permanent

Connective Tissue Connective Tissue FibersFibers
Collagen fibers•Thick, long, straight •Unbranched•Composed of collagen•Great tensile strength •Abundant in dense CT•Hold structures together•Tendons, ligaments
Elastic fibers•Bundles of microfibrils •Embedded in elastin• Fibers branch• Elastic• Vocal cords, air passages
Reticular fibers• Very thin collagenous fibers• Highly branched• Form supportive networks•Least common

Reticularfibers
Fixedmacrophage
Antibodyproducing cell
Blood invessel
Adipocytes(fat cells)
Groundsubstance
Mast cell
Elasticfibers
Freemacrophage
Collagenfibers
Fibroblast
Stem cell
White bloodcell

Types of Connective Types of Connective TissuesTissuesCONNECTIVE TISSUES
CONNECTIVE TISSUE PROPER FLUID CONNECTIVE TISSUES SUPPORTING CONNECTIVE TISSUES
LOOSE DENSE BLOOD LYMPH CARTILAGE BONE
Solid, crystallinematrix
Solid, rubberymatrix
Flows withinlymphaticsystem
Flows withincardiovascular
system
Fibers denselypacked
Fibers createloose, openframework

Connective Tissue Connective Tissue ProperProperLooseLoose
Areolar Tissue• Mainly fibroblasts• Fluid to gel-like matrix• Collagen fibers• Elastic fibers•Highly vascular • Bind skin to structures• Beneath most epithelial• Between muscles
Adipose tissue• Adipocytes• Cushions• Insulates• Store fats• Beneath skin• Behind eyes• Around kidneys and heart

Connective Tissue Connective Tissue ProperProperLooseLoose
Reticular connective tissue• Composed of complex reticular fibers network• Supports framework• Walls of liver, spleen, lymphatic organs

Dense connective tissue• Packed collagenous fibers•Few fibroblasts•Poor blood supply
Connective Tissue ProperConnective Tissue ProperDenseDense
Dense Regular connective tissue• Parallel collagen fibers•Tightly packed fibers•Tendons-attach muscle to bone•Ligaments-attach bone to bone
Dense Irregular connective tissue•Interwoven meshwork with no pattern•Forms organ capsules, covers bone & cartilage & gives strength to skin

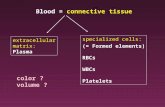
Fluid Connective TissueFluid Connective TissueBlood
•Fluid matrix called plasma• High # of red blood cells•Small # of white blood cells• Platelets-blood clotting• Transports• Defends• Clotting• Flows throughout body in blood vessels• Heart
Lymph• Flows within the lymphatic system•Contains white blood cells•Defends•Transports

Supporting Connective Supporting Connective Tissue-CartilageTissue-Cartilage
Cartilage• Rigid matrix• Chondrocytes in lacunae• Avascular • Three types
• Hyaline• Elastic• Fibrocartilage
Hyaline cartilage• Most abundant• Closely packed collagen fibers• Ends of bones• Nose, respiratory passages• Embryonic skeleton
Elastic cartilage• Flexible• Abundant elastic fibers• External ear, larynx
Fibrocartilage• Very tough• Many collagen fibers• Shock absorber• Intervertebral discs• Pads of knee and pelvic girdle

Hyaline Cartilage
Elastic Cartilage
Fibrocartilage
Three Types of CartilageThree Types of Cartilage

Supporting Supporting Connective Tissue-Connective Tissue-
BoneBoneBone
• Solid matrix• Supports• Protects• Forms blood cells• Attachment for muscles• Skeleton• Osteocytes-bone cells