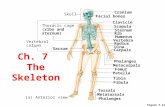
Radiographic technique of Ribs, Clavicle, scapula,sternum, SCJs, ACJs 4 th presentation.
Axial Skeleton – supports the central axis of the body › Skull Skull › Clavicle Clavicle ›...
-
Upload
john-powers -
Category
Documents
-
view
223 -
download
1
Transcript of Axial Skeleton – supports the central axis of the body › Skull Skull › Clavicle Clavicle ›...

Skeletal and Muscular System

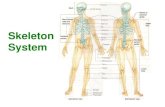
Skeletal System
Axial Skeleton – supports the central axis of the body› Skull› Clavicle› Ribs and Sternum› Vertebrae
Appendicular Skeleton› Arms› Legs

Skeletal System
Skull – protects the brain
Clavicle – hold the upper extremities of the hand
Ribs and Sternum – protects the heart and the lungs

Skeletal System
Vertebrae – protects the spinal cord

Skeletal System Arms
› Humerus upper arm
› Radius and Ulna lower arm
› Carpals wrist
› Metacarpals palm
› Phalanges fingers

Skeletal System Legs
› Femur thigh
› Tibia and Fibula Lower leg
› Tarsals ankle
› Metatarsals sole
› Phalanges toes

Skeletal System Bone Structure
› Periosteum covering of the bone Important for repair
› Compact Bone makes the bone tough
› Spongy Bone Provide spaces for bone marrow
› Bone Marrow Red marrow – production of blood
cells Yellow marrow – composed of fats

Muscular System
Muscles work in pairs (antagonistic)› Myofibrils› Filaments
Actin – thin fiber Myosin – thick fiber
Sliding Filament Theory

Muscular and Skeletal System
Allows movement Gives shape to the body Gives structure to the body

Muscular and Skeletal System
Osteoporosis› Osteoporosis
means “porous bones,” or that bones are losing their density, becoming thinner and more breakable.

Muscular and Skeletal System
Rheumatoid Arthritis› Rheumatoid arthritis
causes swelling, pain, stiffness, and redness in the joints.
› The cause of rheumatoid arthritis is unknown to date, but allegedly triggered by a combination of factors, including genetic susceptibility, viral infection or hormonal changes.

Muscular and Skeletal System
Scoliosis› an abnormal
curvature of the spine.
› Can be a result of poor muscle control or muscle weakness, and traumatic spine injuries

Muscular and Skeletal System
Steroids› Testosterone is commonly
prescribed in the treatment of female breast cancer, and for stimulation of growth, weight gain, and red blood cell production. These are commonly known as "anabolic steroids" because they promote muscle growth. They are also commonly used to help patients recover from a surgery and cancer treatment that resulted in damage to muscle tissue.